BiSeNet V2: 实时语义分割的带引导聚合的双边网络.
BiSeNet的双路分割结构在实时分割的任务中取得了不错的效果,这种网络结构能够保留低级细节和高级语义,同时又不会损害推理速度,很好的权衡了实现准确的语义分割任务和快速的推理速度之间的平衡。因此,提出了基于双路的分段网络-BiSeNetV2来实现实时的语义分割。

相比于初版BiSeNetV1,V2简化了原始结构,使网络更加高效; 使用更加紧凑的网络结构以及精心设计的组件,加深了Semantic Branch的网络,使用更加轻巧的深度可分离卷积来加速模型;设计了更为有效的Aggregation Layer,以增强Semantic Branch和Detail Branch之间的链接。

BiSeNetV2主要包含几个结构:Detail Branch分支、Semantic Branch分支、Aggregation Layer聚合层、Auxiliary Loss分支。
⚪ 细节分支 Detail Branch
对于Detail Branch,依旧使用类VGG的网络结构,这一部分结构较为简单,用于快速下采样并得到细分的feature map。
class DetailBranch(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, detail_channels=(64, 64, 128), in_channels=3):
super(DetailBranch, self).__init__()
self.detail_branch = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(len(detail_channels)):
if i == 0:
self.detail_branch.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, detail_channels[i], 3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(detail_channels[i]),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(detail_channels[i], detail_channels[i], 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(detail_channels[i]),
nn.ReLU(),
)
)
else:
self.detail_branch.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(detail_channels[i-1], detail_channels[i], 3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(detail_channels[i]),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(detail_channels[i], detail_channels[i], 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(detail_channels[i]),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(detail_channels[i], detail_channels[i], 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(detail_channels[i]),
nn.ReLU()
)
)
def forward(self, x):
for stage in self.detail_branch:
x = stage(x)
return x
⚪ 语义分支 Semantic Branch
Semantic Branch与Detail Branch平行,主要用于捕获高级语义信息。在这一个分支中,通道数比较少,因为更多信息可以由Detail Branch提供。由于获取高级语义信息需要上下文的依赖和较大的感受野,所以在这一个分支中,使用快速采样的策略来迅速扩大感受野;使用全局平均池化来嵌入上下文信息。
作者在这部分做了较为精心的设计,主要包括三部分:
- Stem Block用于快速下采样;
- Gather-and-Expansion Layer(GE Layer)用于卷积获取细节信息。
- Context Embedding Block(CE Layer)用于嵌入上下文信息。
Stem Block和CE Block的结构较为简单。
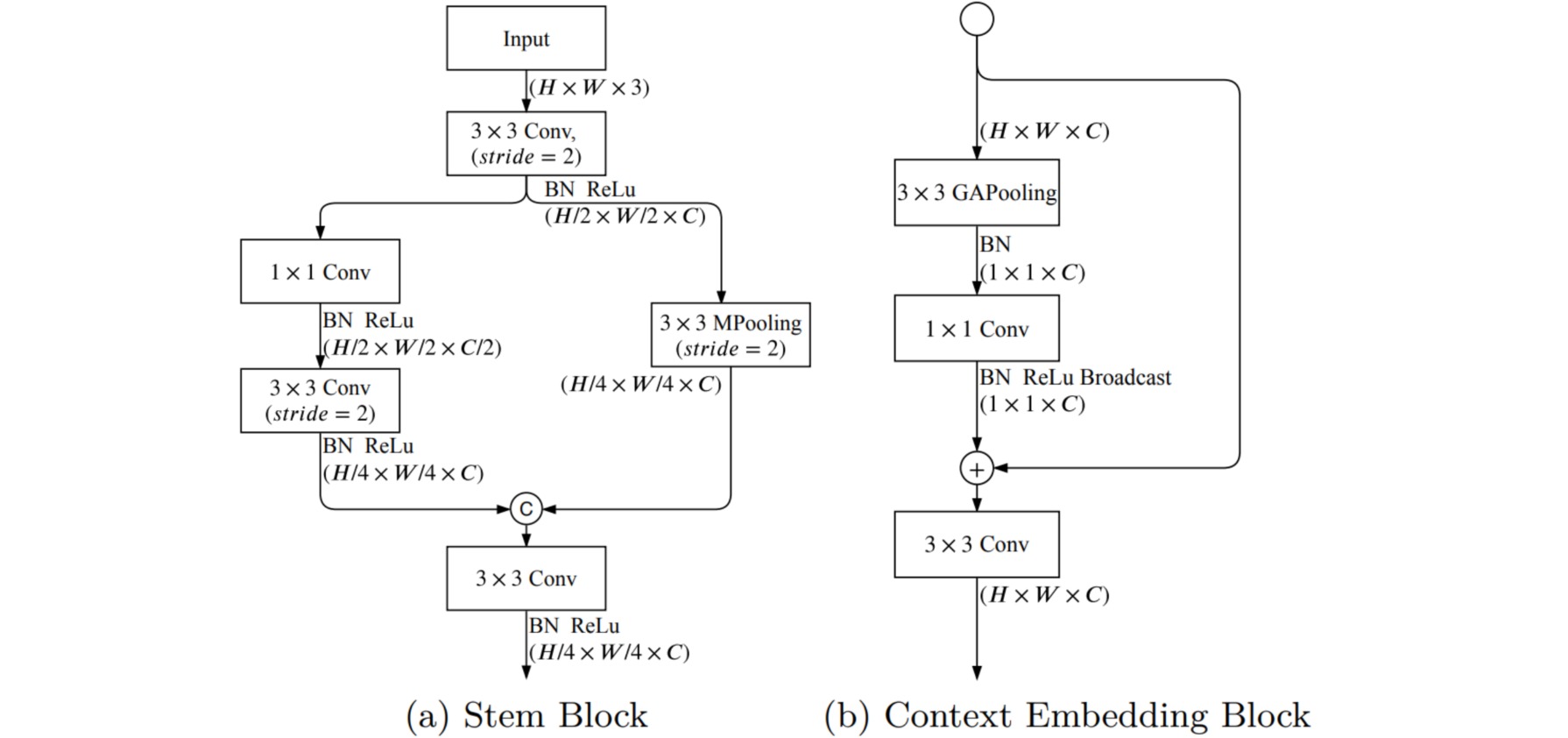
class StemBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=3, out_channels=16):
super(StemBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv_in = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv_branch = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels//2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels//2, out_channels, 3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, ceil_mode=False)
self.fusion = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(2*out_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_in(x)
x_branch = self.conv_branch(x)
x_downsample = self.pool(x)
out = torch.cat([x_branch, x_downsample], dim=1)
out = self.fusion(out)
return out
class CEBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels=16, out_channels=16):
super(CEBlock, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.gap = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channels)
)
self.conv_gap = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels, 1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels)
nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=self.out_channels,
out_channels=self.out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
x = self.gap(x)
x = self.conv_gap(x)
x = identity + x
x = self.conv_last(x)
return x
对于GE Block,分为是否进行下采样的两个模块:不进行下采样的GE Block(b)和进行下采样的GE Block(c)。作者在这里借鉴了MobileNetv2中的倒瓶颈结构设计,为了减少计算量,中间使用一个深度可分离卷积。

class depthwise_separable_conv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride):
super(depthwise_separable_conv, self).__init__()
self.depthwise = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=in_channels)
self.pointwise = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.depthwise(x)
out = self.pointwise(out)
return out
class GELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, exp_ratio=6, stride=1):
super(GELayer, self).__init__()
mid_channel = in_channels * exp_ratio
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
if stride == 1:
self.dwconv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channel, 3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=in_channels),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channel),
nn.ReLU(),
depthwise_separable_conv(mid_channel, mid_channel, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channel),
)
self.shortcut = None
else:
self.dwconv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channel, 3, stride=1, padding=1, groups=in_channels,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channel),
nn.ReLU(),
depthwise_separable_conv(mid_channel, mid_channel, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channel),
depthwise_separable_conv(mid_channel, mid_channel, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channel),
)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
depthwise_separable_conv(in_channels, out_channels, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(mid_channel, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
self.act = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.dwconv(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
if self.shortcut is not None:
shortcut = self.shortcut(identity)
x = x + shortcut
else:
x = x + identity
x = self.act(x)
return x
Semantic Branch的整体结构:
class SemanticBranch(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, semantic_channels=(16, 32, 64, 128), in_channels=3, exp_ratio=6):
super(SemanticBranch, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.semantic_channels = semantic_channels
self.semantic_stages = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(len(semantic_channels)):
if i == 0:
self.semantic_stages.append(StemBlock(self.in_channels, semantic_channels[i]))
elif i == (len(semantic_channels) - 1):
self.semantic_stages.append(
nn.Sequential(
GELayer(semantic_channels[i - 1], semantic_channels[i], exp_ratio, 2),
GELayer(semantic_channels[i], semantic_channels[i], exp_ratio, 1),
GELayer(semantic_channels[i], semantic_channels[i], exp_ratio, 1),
GELayer(semantic_channels[i], semantic_channels[i], exp_ratio, 1)
)
)
else:
self.semantic_stages.append(
nn.Sequential(
GELayer(semantic_channels[i - 1], semantic_channels[i],
exp_ratio, 2),
GELayer(semantic_channels[i], semantic_channels[i],
exp_ratio, 1)
)
)
self.semantic_stages.append(CEBlock(semantic_channels[-1], semantic_channels[-1]))
def forward(self, x):
semantic_outs = []
for semantic_stage in self.semantic_stages:
x = semantic_stage(x)
semantic_outs.append(x)
return semantic_outs
⚪ 聚合层 Aggregation Layer
Aggregation Layer接受了Detail Branch和Semantic Branch的结果,通过下图中的一系列操作进行特征融合。

class AggregationLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(AggregationLayer, self).__init__()
self.Conv_DetailBranch_1 = nn.Sequential(
depthwise_separable_conv(in_channels, out_channels, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
)
self.Conv_DetailBranch_2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
)
self.Conv_SemanticBranch_1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=4, mode="bilinear", align_corners=True),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.Conv_SemanticBranch_2 = nn.Sequential(
depthwise_separable_conv(in_channels, out_channels, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.conv_out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
)
def forward(self, Detail_x, Semantic_x):
DetailBranch_1 = self.Conv_DetailBranch_1(Detail_x)
DetailBranch_2 = self.Conv_DetailBranch_2(Detail_x)
SemanticBranch_1 = self.Conv_SemanticBranch_1(Semantic_x)
SemanticBranch_2 = self.Conv_SemanticBranch_2(Semantic_x)
out_1 = torch.matmul(DetailBranch_1, SemanticBranch_1)
out_2 = torch.matmul(DetailBranch_2, SemanticBranch_2)
out_2 = F.interpolate(out_2, scale_factor=4, mode="bilinear", align_corners=True)
out = out_1+out_2
out = self.conv_out(out)
return out
⚪ Auxiliary Loss
作者在Semantic Branch中引出了几个Auxiliary Loss分支,对比了集中Auxiliary Loss组合的性能,得出如下结果。其中检测头的实现比较简单。

class SegHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, num_classes):
super().__init__()
self.cls_seg = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(channels, num_classes, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cls_seg(x)
⚪ BiSeNet V2
BiSeNet V2的整体结构实现如下:
class BiSeNetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels=3,
detail_channels=(64, 64, 128),
semantic_channels=(16, 32, 64, 128),
semantic_expansion_ratio=6,
aggregation_channels=128,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3, 4),
num_classes = 3):
super(BiSeNetV2, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.detail_channels = detail_channels
self.semantic_expansion_ratio = semantic_expansion_ratio
self.semantic_channels = semantic_channels
self.aggregation_channels = aggregation_channels
self.out_indices = out_indices
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.detail = DetailBranch(detail_channels=self.detail_channels, in_channels=self.in_channels)
self.semantic = SemanticBranch(semantic_channels=self.semantic_channels, in_channels=self.in_channels,exp_ratio=self.semantic_expansion_ratio)
self.AggregationLayer = AggregationLayer(in_channels=self.aggregation_channels, out_channels=self.aggregation_channels)
self.seg_head_aggre = SegHead(semantic_channels[-1], self.num_classes)
self.seg_heads = nn.ModuleList()
self.seg_heads.append(self.seg_head_aggre)
for channel in semantic_channels:
self.seg_heads.append(SegHead(channel, self.num_classes))
def forward(self, x):
_, _, h, w = x.size()
x_detail = self.detail(x)
x_semantic_lst = self.semantic(x)
x_head = self.AggregationLayer(x_detail, x_semantic_lst[-1])
outs = [x_head] + x_semantic_lst[:-1]
outs = [outs[i] for i in self.out_indices]
out = tuple(outs)
seg_out = []
for index, stage in enumerate(self.seg_heads):
seg_out.append(F.interpolate(stage(out[index]),size=(h,w), mode="bilinear", align_corners=True))
return seg_out


