CondConv:用于高效推理的条件参数化卷积.
标准的卷积具有参数共享的特点。本文作者设计了条件参数化卷积(Conditionally Parameterized Convolution, CondConv),在卷积层设置多套卷积核,在推断时根据输入决定各套卷积核的权重,最终加权求和得到一个新的卷积核,执行一次卷积。
CondConv可以等效为一个混合专家系统(Mixture of Experts, MoE),相当于多个标准卷积的线性组合,组合权重通过梯度下降算法学习。通过增大专家数量可以有效地提升模型容量,同时专家只需要进行一次组合,能够保持高效推理。

各套卷积核的权重是通过全局平均池化和全连接层构造的,并通过Sigmoid函数归一化;相当于对卷积核施加注意力模块:
\[\alpha = \text{sigmoid}(\text{GlobalAveragePool}(x)R)\]在训练过程中,由于每张输入图像的动态卷积核都是不一样的,所以在一个batch里并行计算是困难的。CondConv的解决方法是首先把batch维度堆叠到通道维度,然后通过组卷积实现。
CondConv所引入的计算量比较有限,每组CondConv只相当于多引入了一次乘加操作,能够在不增加过多计算量的前提下提高模型的表现:
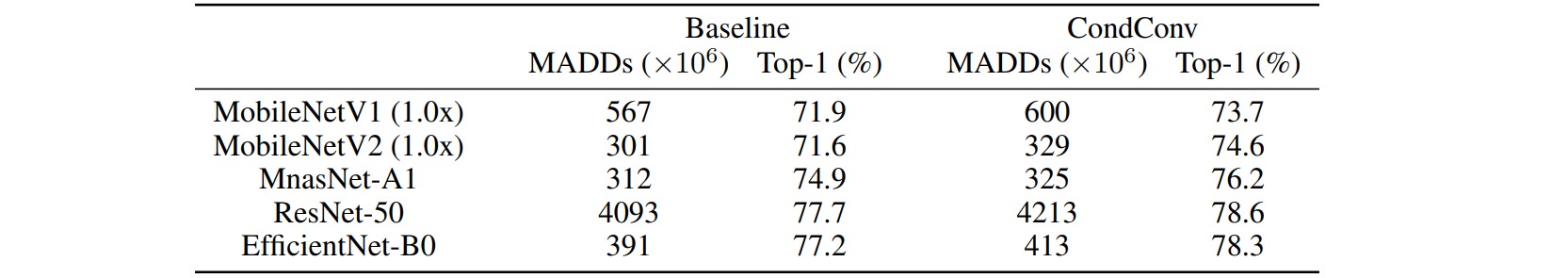
作者在MobileNet模型的基础上进行实验,分别设置$(1,2,4,8,16,32)$个专家,并调整模型宽度为$(0.25,0.5,0.75,1)$倍,对应的不同模型的乘加计算量和准确率如下:

import functools
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.nn.modules.conv import _ConvNd
from torch.nn.modules.utils import _pair
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
class _attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_experts, out_channels, kernel_size, r=4):
super(_attention, self).__init__()
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.fc = nn.Linear(in_channels, in_channels//r)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.fc_as = nn.Linear(in_channels//r, kernel_size*kernel_size)
self.fc_ac = nn.Linear(in_channels//r, in_channels)
self.fc_af = nn.Linear(in_channels//r, out_channels)
self.fc_an = nn.Linear(in_channels//r, num_experts)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.flatten(x)
x = self.fc(x)
_as = self.fc_as(x)
_ac = self.fc_ac(x)
_af = self.fc_af(x)
_an = self.fc_an(x)
return (
torch.sigmoid(_as).view(self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size),
torch.sigmoid(_ac),
torch.sigmoid(_af),
torch.softmax(_an, dim=0),)
class ODConv2D(_ConvNd):
r"""
in_channels (int): Number of channels in the input image
out_channels (int): Number of channels produced by the convolution
kernel_size (int or tuple): Size of the convolving kernel
stride (int or tuple, optional): Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
padding (int or tuple, optional): Zero-padding added to both sides of the input. Default: 0
padding_mode (string, optional): ``'zeros'``, ``'reflect'``, ``'replicate'`` or ``'circular'``. Default: ``'zeros'``
dilation (int or tuple, optional): Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
groups (int, optional): Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
bias (bool, optional): If ``True``, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: ``True``
num_experts (int): Number of experts per layer
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1,
padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1,
bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', num_experts=3, dropout_rate=0.2):
kernel_size = _pair(kernel_size)
stride = _pair(stride)
padding = _pair(padding)
dilation = _pair(dilation)
super(ODConv2D, self).__init__(
in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation,
False, _pair(0), groups, bias, padding_mode)
# 全局平均池化
self._avg_pooling = functools.partial(F.adaptive_avg_pool2d, output_size=(1, 1))
# 注意力函数
self._attention_fn = _attention(in_channels, num_experts, out_channels, kernel_size[0])
# 动态卷积层的权重
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
num_experts, out_channels, in_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
self.reset_parameters()
def _conv_forward(self, input, weight):
if self.padding_mode != 'zeros':
return F.conv2d(F.pad(input, self._padding_repeated_twice, mode=self.padding_mode),
weight, self.bias, self.stride,
_pair(0), self.dilation, self.groups)
return F.conv2d(input, weight, self.bias, self.stride,
self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
def forward(self, inputs): # [b, c, h, w]
res = []
for input in inputs:
input = input.unsqueeze(0) # [1, c, h, w]
pooled_inputs = self._avg_pooling(input) # [1, c, 1, 1]
_as, _ac, _af, _an = self._attention_fn(pooled_inputs)
_as = _as[None, None, None, :, :]
_ac = _ac[None, None, :, None, None]
_af = _af[None, :, None, None, None]
_an = _an[:, None, None, None, None]
kernels = torch.sum(_as * _ac * _af * _an * self.weight, 0)
out = self._conv_forward(input, kernels)
res.append(out)
return torch.cat(res, dim=0)


