SIoU Loss:学习更强大的边界框回归.
传统的目标检测损失函数依赖于边界框回归指标的聚合,例如预测框和真实框的距离、重叠区域和纵横比(即 GIoU、CIoU等)。然而,迄今为止提出和使用的方法都没有考虑到所需真实框与预测框之间不匹配的方向。这种不足导致收敛速度较慢且效率较低,因为预测框可能在训练过程中“四处游荡”并最终产生更差的模型。
针对以上问题,本文提出了SIOU损失函数,其中考虑到所需回归之间的向量角度。通过考虑不匹配的方向,极大地帮助了训练过程,因为它可以让预测框很快地漂移到最近的轴,并且随后的方法只需要一个坐标 X 或 Y 的回归。简而言之,添加角度惩罚成本有效地减少了边界框回归的总自由度。
SIoU损失函数由4个损失函数组成:
- Angle损失
- Distance损失
- Shape损失
- IoU损失
⚪ 角度损失
角度损失定义回归框$B$与目标框$B_{GT}$的夹角小于$\alpha$时,向最小$\alpha$收敛;反之向最小$\beta$收敛。损失函数定义为:
\[\Lambda = 1-2 \cdot \sin^2 \left( \arcsin(x) - \frac{\pi}{4} \right)\]其中:
\[\begin{aligned} x &= \frac{c_h}{\sigma} = \sin(\alpha) \\ \sigma &= \sqrt{(b_{c_x}^{gt}-b_{c_x})^2 + (b_{c_y}^{gt}-b_{c_y})^2} \\ c_h &= \max(b_{c_y}^{gt},b_{c_y})- \min(b_{c_y}^{gt},b_{c_y}) \end{aligned}\]
简化角度损失:
\[\begin{aligned} \Lambda &= 1-2 \cdot \sin^2 \left( \arcsin(x) - \frac{\pi}{4} \right) \\ &= 1-2 \cdot \sin^2 \left( \arcsin(\sin(\alpha)) - \frac{\pi}{4} \right) \\ &= 1-2 \cdot \sin^2 \left( \alpha - \frac{\pi}{4} \right) \\ &= \cos^2 \left( \alpha - \frac{\pi}{4} \right) - \sin^2 \left( \alpha - \frac{\pi}{4} \right) \\ &= \cos \left( 2\alpha - \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \\ &= \sin \left( 2\alpha \right) \\ \end{aligned}\]上式表明损失是当前角度的2倍取sin值,在0度的时候取最小值。在$\alpha=\frac{\pi}{4}$时取最大值。通过最小化角度损失使得检测框尽量沿着X 或 Y 轴方向回归。
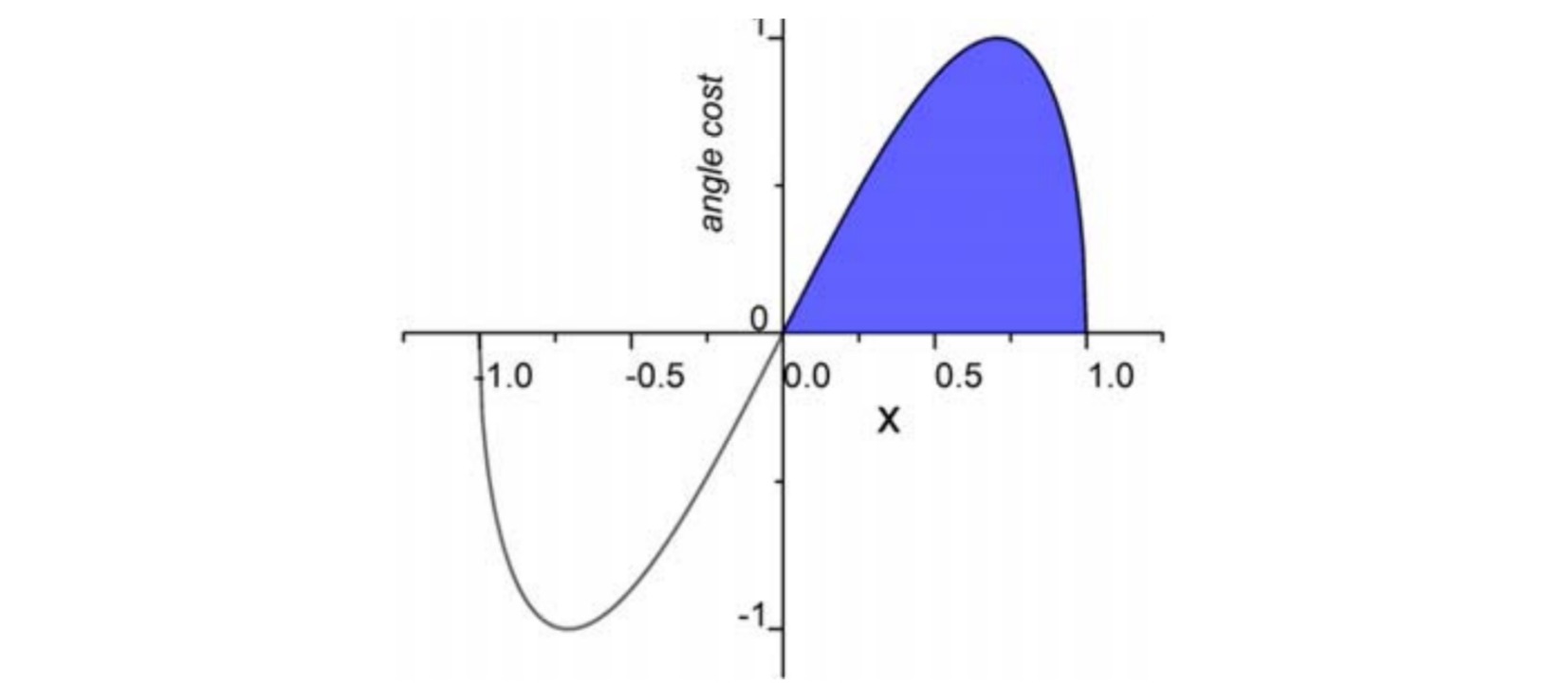
⚪ 距离损失
角度损失只能衡量方向,不能衡量距离。如果一个角度是平角但是距离很长与一个相反情况的肯定优先选择近的。作者将角度损失同时考虑到距离损失中,保证距离与角度的平衡。距离损失计算为:
\[\begin{aligned} \Delta &= \sum_{t=x,y} (1-e^{-\gamma \rho_t}) \\ \rho_x &= \left( \frac{b_{c_x}^{gt}-b_{c_x}}{c_w} \right)^2 \\ \rho_y &= \left( \frac{b_{c_y}^{gt}-b_{c_y}}{c_h} \right)^2 \\ \gamma &= 2 - \Lambda \end{aligned}\]距离损失采用指数形式,其中$\rho_t$是边界框中心点的距离,使用2次幂来赋权重,说明距离的影响要大于角度的影响。

⚪ 形状损失
形状损失分别从长宽衡量回归框的形状与标签框是否相似,并惩罚两个维度上的差值:
\[\begin{aligned} \Omega &= \sum_{t=w,h} (1-e^{-\omega_t})^{\theta} \\ \omega_w &= \frac{|w^{gt}-w|}{\max(w^{gt},w)} \\ \omega_h &= \frac{|h^{gt}-h|}{\max(h^{gt},h)} \\ \end{aligned}\]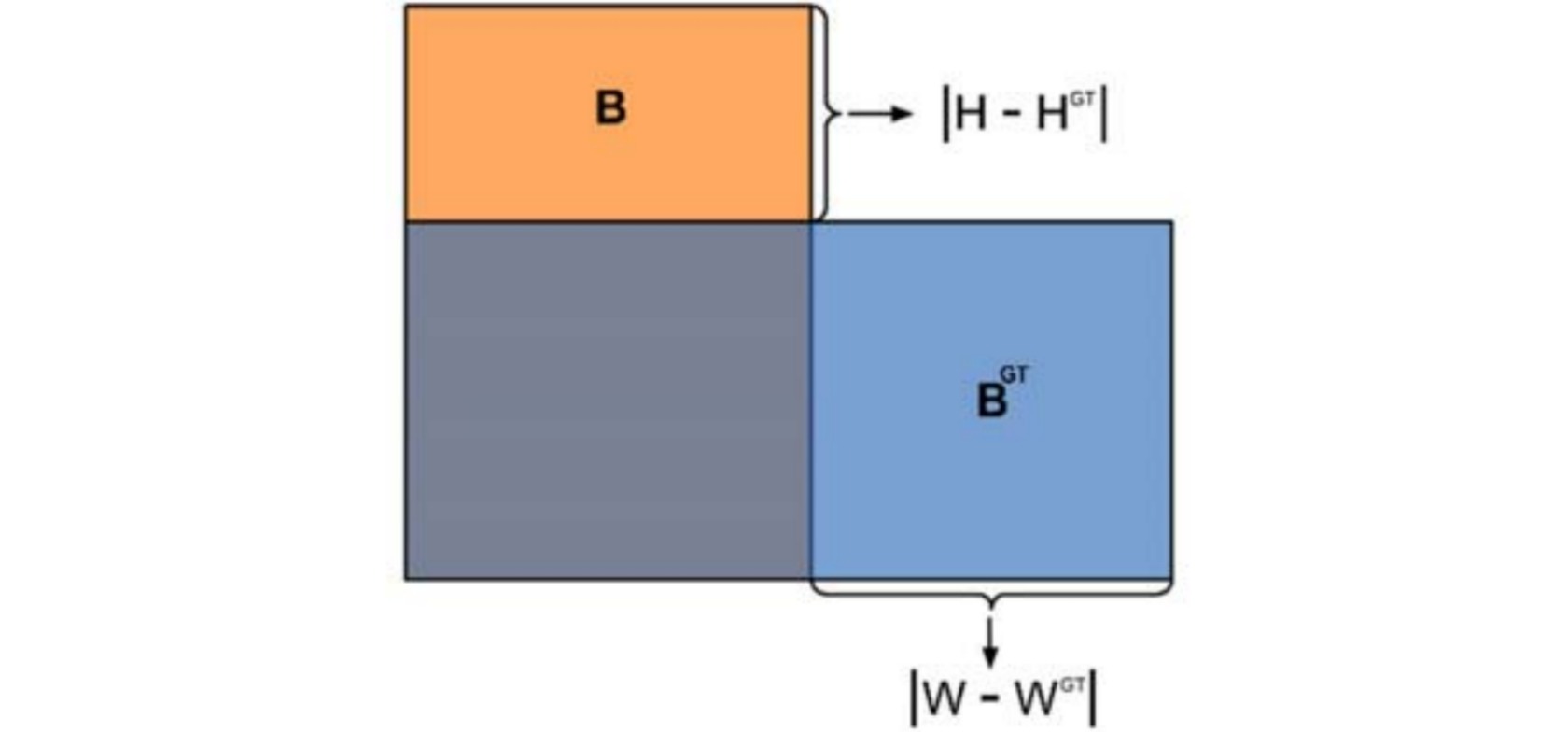
⚪ 总损失
总损失函数为:
\[L = 1 - IoU + \frac{\Delta + \Omega}{2}\]def bbox_siou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True, eps=1e-7):
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
iou = inter / union
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
s_cw = (b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) * 0.5
s_ch = (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) * 0.5
sin_alpha_1 = ch / s_ch
sin_alpha_2 = cw / s_cw
sin_alpha = torch.where(sin_alpha_1 > torch.pi/4, sin_alpha_2, sin_alpha_1)
angle_cost = torch.cos(torch.arcsin(sin_alpha) * 2 - math.pi / 2)
gamma = 2 - angle_cost
rho_x = (s_cw / cw) ** 2
rho_y = (s_ch / ch) ** 2
distance_cost = 1 - torch.exp(-1 * gamma * rho_x) + 1 - torch.exp(-1 * gamma * rho_y)
omiga_w = torch.abs(w1 - w2) / torch.max(w1, w2)
omiga_h = torch.abs(h1 - h2) / torch.max(h1, h2)
shape_cost = torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_w), 4) + torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_h), 4)
return iou - 0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost)


