GFocal Loss: 为密集目标检测学习合格且分散的边界框.
- paper:Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection
目前比较强力的单阶段目标检测器最终的输出基本会包含3个表示:
- 分类表示:目标的类别得分(classification score)
- 检测框表示:边界框的回归结果(bbox regression)
- 检测框的质量估计(IoU/centerness score)
1. 目前存在的问题
现有的表示形式存在如下问题:
- 分类预测分值和质量评估分值训练测试不一致
- bbox回归采用的表示不够灵活,没有办法建模复杂场景下不确定性
① classification score 和 IoU/centerness score 训练测试不一致
- 用法不一致。训练的时候,分类和质量估计独立地训练;但测试的时候却又是乘在一起作为NMS score排序的依据;
- 对象不一致。分类分支能够使得少量的正样本和大量的负样本一起成功训练,但是质量估计通常就只针对正样本训练。

② bbox regression 采用的表示不够灵活,没有办法建模复杂场景下的uncertainty
在复杂场景中,边界框的表示具有很强的不确定性,而现有的框回归本质都是建模了非常单一的狄拉克分布,应该用一种general的分布去建模边界框的表示。

2. 解决方案
针对目前目标检测存在的两个问题,提出了两个解决办法:
- 将bbox预测质量和分类分支loss联合表示,解决两分支独立训练,联合测试不一致问题
- 采用自发学习的灵活分布建模形式来表示bbox不确定性,具体是采用softmax+积分形式,相当于把回归问题转换为分类问题
① 将bbox预测质量和分类分支loss联合表示
对于第一个问题,为了保证训练和测试的一致性,同时还能够兼顾分类score和质量预测score都能够训练到所有的正负样本,需要将两者的表示进行联合。从物理上依然还是保留分类的向量,但是对应类别位置的置信度的物理含义不再是分类的score,而是改为质量预测的score。这样就做到了两者的联合表示。
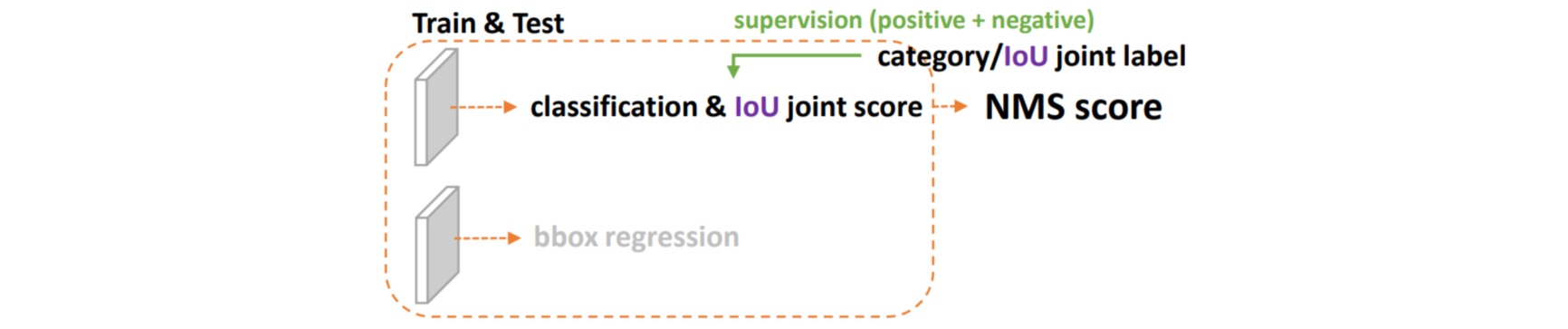
对于分类-质量联合表示,label变成了0~1之间的连续值。如果要引入Focal Loss平衡正负、难易样本的特性,需要让其支持连续数值的监督,因此需要对Focal Loss在连续label上拓展,称为Quality Focal Loss (QFL)。Focal Loss表示为:
\[FL(p) = -(1-p_t)^\gamma \log(p_t) \\ p_t = \begin{cases} p, & y=1 \\ 1-p, & y=0 \end{cases}\]QFL则将其修改为:
\[QFL(p) = -|y-p|^\beta \left( y\log p + (1-y) \log(1-p) \right)\]其中$y$为$0$~$1$的质量标签,$\sigma$为预测。注意QFL的全局最小解即是$\sigma = y$,这样交叉熵部分变为完整的交叉熵。调节因子为距离绝对值的幂次函数,实验中发现一般取$\beta = 2$为最优。
def quality_focal_loss(pred, target, beta=2.0):
"""
Args:
pred (torch.Tensor): Predicted joint representation of classification
and quality (IoU) estimation with shape (N, C), C is the number of
classes.
target (tuple([torch.Tensor])): Target category label with shape (N,)
and target quality label with shape (N,).
beta (float): The beta parameter for calculating the modulating factor.
Defaults to 2.0.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Loss tensor with shape (N,).
"""
assert len(target) == 2, """target for QFL must be a tuple of two elements,
including category label and quality label, respectively"""
# label denotes the category id, score denotes the quality score
label, score = target # label(N) 类别,score(N),预测bbox和gt bbox的iou
# negatives are supervised by 0 quality score
pred_sigmoid = pred.sigmoid() # (N,class_num)
scale_factor = pred_sigmoid
zerolabel = scale_factor.new_zeros(pred.shape)
# 先假设所有label都是负样本,计算bce loss,乘上sigmoid^beta次方,达到focal效应
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
pred, zerolabel, reduction='none') * scale_factor.pow(beta)
# FG cat_id: [0, num_classes -1], BG cat_id: num_classes
bg_class_ind = pred.size(1)
# 找出正样本索引
pos = ((label >= 0) & (label < bg_class_ind)).nonzero().squeeze(1)
pos_label = label[pos].long()
# positives are supervised by bbox quality (IoU) score
scale_factor = score[pos] - pred_sigmoid[pos, pos_label] # 正样本focal值
# 计算正样本处的bce loss,注意label=score,而不是1
loss[pos, pos_label] = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
pred[pos, pos_label], score[pos],
reduction='none') * scale_factor.abs().pow(beta)
loss = loss.sum(dim=1, keepdim=False) # (N,class_num)在1维度直接求和,变成(N,)
return loss
① 采用自发学习的灵活分布建模形式来表示bbox不确定性
对于第二个问题,选择直接回归一个任意分布来建模框的表示。在连续域上回归是不可能的,所以可以用离散化的方式,通过softmax来实现即可。
首先作者对所有 gt bbox 映射到特征图维度,并计算所有coco数据集中正样本的回归范围,如下所示:

可以发现最大值大概可以设置为$16$,也就是说分布长度可以设置为$16+1$,而且需要特别指出不同的数据集由于分布不一致,需要针对数据特点重新确定这个超参。
对于任意分布来建模框的表示,它可以用积分形式(通过求和实现)直接转化得到浮点坐标,嵌入到任意已有的和框回归相关的损失函数上。不过如果分布过于任意,网络学习的效率可能会不高,原因是一个积分目标可能对应了无穷多种分布模式。
考虑到真实的分布通常不会距离标注的位置太远,所以额外引入Distribution Focal Loss (DFL),希望网络能够快速地聚焦到标注位置附近的数值,使得他们概率尽可能大。其形式上与QFL的右半部分很类似,含义是以类似交叉熵的形式去优化与标签$y$最接近的一左一右两个位置的概率,从而让网络快速地聚焦到目标位置的邻近区域的分布中去。
\[DFL(S_i, S_{i+1}) = -\left( (y_{i+1}-y)\log S_i + (y-y_i) \log S_{i+1} \right)\]$y_i$和$y_{i+1}$是浮点值$y$的左右整数值,$S$是输出分布,长度为$17$,可以看出这本质就是一个bce loss,通过计算全局最优解是:
\[S_i=\frac{y_{i+1}-y}{y_{i+1}-y_i}, S_{i+1}=\frac{y-y_i}{y_{i+1}-y_i}\]学出来的分布理论上是在真实浮点坐标的附近,并且以线性插值的模式得到距离左右整数坐标的权重。
def distribution_focal_loss(pred, label):
"""
Args:
pred (torch.Tensor): Predicted general distribution of bounding boxes
(before softmax) with shape (N, n+1), n is the max value of the
integral set `{0, ..., n}` in paper.
label (torch.Tensor): Target distance label for bounding boxes with
shape (N,).
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Loss tensor with shape (N,).
"""
dis_left = label.long() # 坐标整数值
dis_right = dis_left + 1 # 右边整数值
# 线性权重
weight_left = dis_right.float() - label
weight_right = label - dis_left.float()
# 两个bce loss,并且加权,促使学到的分布是双峰分布,提高优化效率
loss = F.cross_entropy(pred, dis_left, reduction='none') * weight_left \
+ F.cross_entropy(pred, dis_right, reduction='none') * weight_right
return loss
QFL和DFL可以统一地表示为GFL (Generalized Focal Loss):
\[GFL\left(p_{y_l}, p_{y_r}\right)=-\left|y-\left(y_l p_{y_l}+y_r p_{y_r}\right)\right|^\beta\left(\left(y_r-y\right) \log \left(p_{y_l}\right)+\left(y-y_l\right) \log \left(p_{y_r}\right)\right)\]


