人体姿态估计中的分布敏感的坐标表示.
在Heatmap-based方法中,对预测热图解码时是把模型输出的高斯概率分布图用Argmax得到最大相应点坐标。由于Argmax操作最的结果只能是整数,这就导致了经过下采样的特征图永远不可能得到输入图片尺度的坐标精度,因此产生了量化误差(quantization error)。
为了缓解量化误差,一些方法将预测坐标从最大值点向第二大值点方向移动 0.25 像素,然而这种误差补偿方法是粗糙的。本文提出了Distribution-Aware coordinate Representation of Keypoint (DARK)方法,利用高斯分布的泰勒展开来缓解热图回归的量化误差。
泰勒展开是指对于函数图像上每一个点,由于点是连续的,因而都蕴含着关于周围点的信息,通过该点的导数可以还原周围的信息,理论上来说阶数越高能还原出来的信息就越多,从而越逼近真实函数值。由于高斯分布是已知的信息,所以很容易就能求出输出图像最大值点上的一阶导数和二阶导数,从而对结果进行信息补充,在一定范围内修正量化误差。
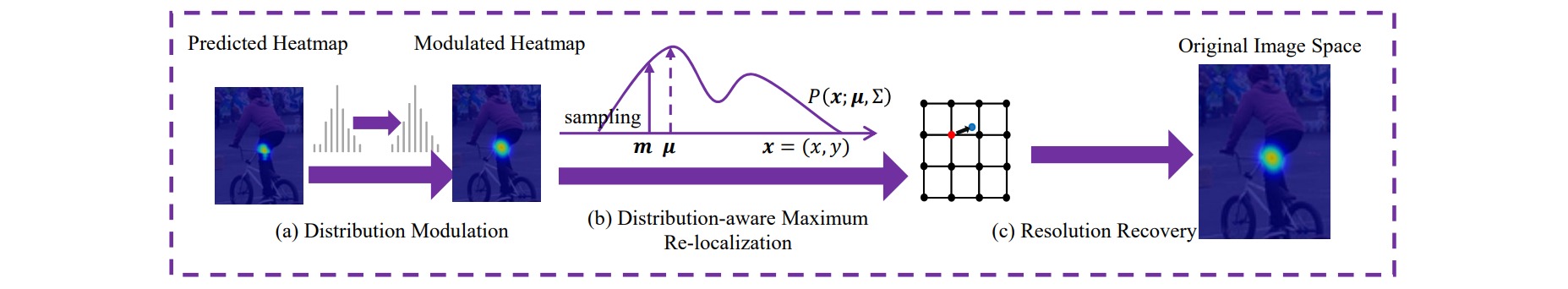
假设关键点的真实坐标为$\mu=(\mu_x,\mu_y)$,则没有误差时的预测热图\(\mathcal{H}\)应该表示为:
\[\mathcal{H}(x,y) = e^{-\frac{(x-\mu_x)^2+(y-\mu_y)^2}{2\sigma^2}}\]对热图\(\mathcal{H}\)在最大值点$m$处进行泰勒展开:
\[\mathcal{H}(p) = \mathcal{H}(m) + \mathcal{H}'(m)(p-m) + \frac{1}{2}\mathcal{H}''(m)(p-m)^2 + \mathcal{O}(p^2)\]上式两端对$p$求导得:
\[\mathcal{H}'(p) \approx \mathcal{H}'(m) + \mathcal{H}''(m)(p-m)\]代入真实坐标$\mu$,并注意到\(\mathcal{H}'(\mu)=0\),因此有:
\[\mu = m-(\mathcal{H}''(m))^{-1} \mathcal{H}'(m)\]注意到上述分析丢弃了大于二阶的多项式项,因此DARK可以适用于热图概率分布函数的对数多项式需不高于二次,比如高斯热图的对数形式。通常模型的预测热图并不是良好的高斯形式,因此可以首先对输出热图应用高斯模糊。

DARK的解码方式可以在不需要重新训练的情况下,提高现有方法的推理准确率。
def get_max_preds(batch_heatmaps):
'''
get predictions from score maps
heatmaps: numpy.ndarray([batch_size, num_joints, height, width])
'''
batch_size = batch_heatmaps.shape[0]
num_joints = batch_heatmaps.shape[1]
width = batch_heatmaps.shape[3]
heatmaps_reshaped = batch_heatmaps.reshape((batch_size, num_joints, -1))
idx = np.argmax(heatmaps_reshaped, 2)
maxvals = np.amax(heatmaps_reshaped, 2)
maxvals = maxvals.reshape((batch_size, num_joints, 1))
idx = idx.reshape((batch_size, num_joints, 1))
preds = np.tile(idx, (1, 1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
preds[:, :, 0] = (preds[:, :, 0]) % width
preds[:, :, 1] = np.floor((preds[:, :, 1]) / width)
pred_mask = np.tile(np.greater(maxvals, 0.0), (1, 1, 2))
pred_mask = pred_mask.astype(np.float32)
preds *= pred_mask
return preds, maxvals
def gaussian_blur(hm, kernel=3):
border = (kernel - 1) // 2
batch_size = hm.shape[0]
num_joints = hm.shape[1]
height = hm.shape[2]
width = hm.shape[3]
for i in range(batch_size):
for j in range(num_joints):
origin_max = np.max(hm[i,j])
dr = np.zeros((height + 2 * border, width + 2 * border))
dr[border: -border, border: -border] = hm[i,j].copy()
dr = cv2.GaussianBlur(dr, (kernel, kernel), 0)
hm[i,j] = dr[border: -border, border: -border].copy()
hm[i,j] *= origin_max / np.max(hm[i,j])
return hm
def taylor(hm, coord):
heatmap_height = hm.shape[0]
heatmap_width = hm.shape[1]
px = int(coord[0])
py = int(coord[1])
if 1 < px < heatmap_width-2 and 1 < py < heatmap_height-2:
dx = 0.5 * (hm[py][px+1] - hm[py][px-1])
dy = 0.5 * (hm[py+1][px] - hm[py-1][px])
dxx = 0.25 * (hm[py][px+2] - 2 * hm[py][px] + hm[py][px-2])
dxy = 0.25 * (hm[py+1][px+1] - hm[py-1][px+1] - hm[py+1][px-1] \
+ hm[py-1][px-1])
dyy = 0.25 * (hm[py+2*1][px] - 2 * hm[py][px] + hm[py-2*1][px])
derivative = np.matrix([[dx],[dy]])
hessian = np.matrix([[dxx,dxy],[dxy,dyy]])
if dxx * dyy - dxy ** 2 != 0:
hessianinv = hessian.I
offset = -hessianinv * derivative
offset = np.squeeze(np.array(offset.T), axis=0)
coord += offset
return coord
def get_final_preds(hm):
'''
hm: numpy.ndarray([batch_size, num_joints, height, width])
'''
coords, maxvals = get_max_preds(hm)
hm = gaussian_blur(hm)
hm = np.maximum(hm, 1e-10)
hm = np.log(hm)
for n in range(coords.shape[0]):
for p in range(coords.shape[1]):
coords[n,p] = taylor(hm[n][p], coords[n][p])
return coords, maxvals


