Faster R-CNN:通过区域提议网络实现实时目标检测.
R-CNN和Fast R-CNN通过选择搜索算法生成候选区域,比较耗时。Faster R-CNN通过卷积神经网络模型来实现区域提议算法,这是通过在Fast R-CNN中引入区域提议网络(Region Proposal Network, RPN)实现的。
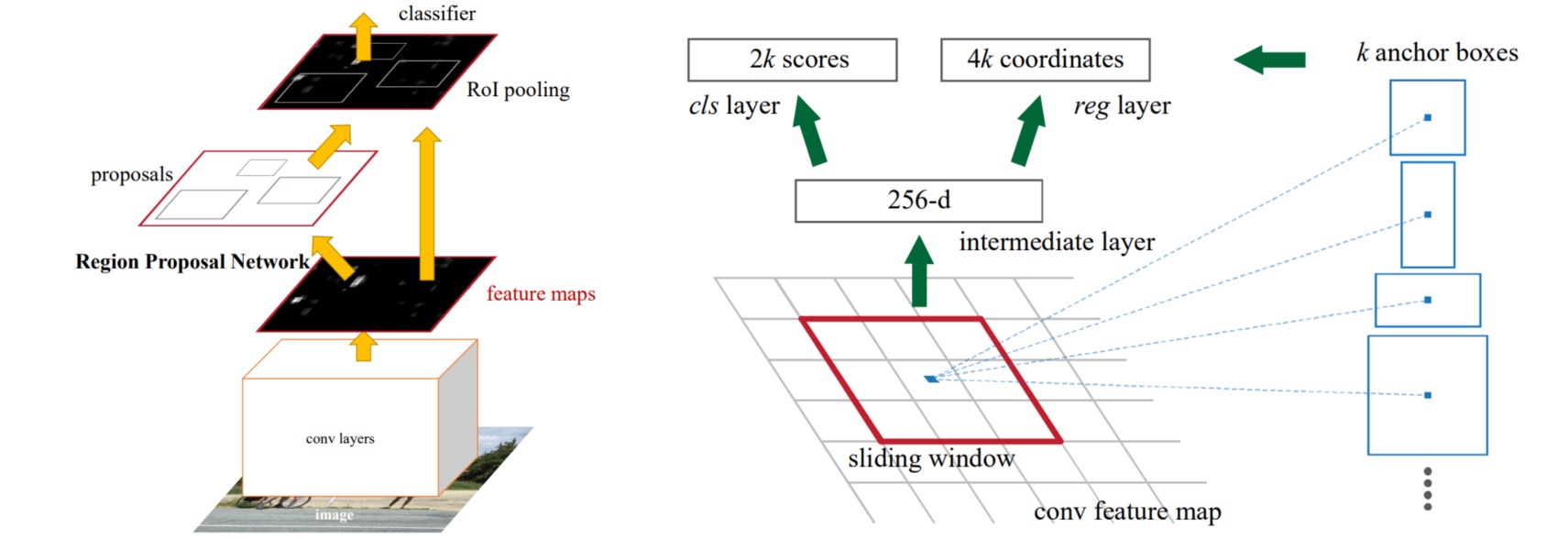
1. Faster RCNN的网络结构
Faster RCNN模型的工作流程如下:
- 把任意大小的图像缩放至固定大小(如$800\times 600$);
- 使用预训练的卷积神经网络提取特征映射(feature maps);
- 通过RPN生成区域提议(region proposals),即对预设anchor进行类别识别(正类或负类)和边界框回归;
- 通过RoI Pooling根据特征映射和区域提议提取提议特征映射(proposal feature map);
- 通过全连接层执行提议特征映射的目标类别识别和边界框回归。

(1)预训练卷积网络
预训练卷积网络选择在通用的图像分类任务(如$1000$类的ImageNet)上预训练的卷积神经网络(如AlexNet, VGGNet, ResNet)的特征提取部分(全卷积结构);以VGGNet16模型为例,网络包括$13$个卷积层(ReLU激活)和$4$个最大池化层。所有卷积核设置为$3\times 3$,池化步长为$2$;则模型对输入图像进行$2^4=16$倍下采样。若输入尺寸为$800\times 600$,则输出特征尺寸为$50\times 38$。
(2)RPN
RPN接收下采样的特征映射,使用一个$3 \times 3$卷积层进行特征增强。由于已经人为设置了anchor(参考下一节),RPN使用两个$1\times 1$卷积分别预测anchor的类别(positive和negative)和anchor的边界框位置偏移量。并通过proposal层综合positive anchors和对应边界框回归偏移量获取proposals。这一步已经完成了目标定位功能。
⚪ RPN的前向过程
在论文原文中使用的是ZFNet,其最后一个卷积层的输出特征维度是$256$,对应特征图上的每个像素都是$256$维特征向量。之后只用$3\times 3$卷积聚合局部空间信息,特征维度保持不变。
由于对特征映射的每个位置预设了$k=9$个anchor,因此RPN需要在特征的每个像素位置处预测$9$个anchor的类别和边界框位置偏移量。通过$1\times 1$卷积层分别预测类别特征(特征维度是$2k=18$)和位置偏移(特征维度是$4k=36$)。
对类别特征应用softmax后获得anchor的分类结果,通常认为postive anchors检测到目标。也有实现用sigmoid代替softmax,输出$k=9$维度的特征进行分类。在训练时会在anchor中随机选取$128$个postive anchors和$128$个negative anchors进行训练。
class RegionProposalNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels = 512,
mid_channels = 512,
ratios = [0.5, 1, 2],
anchor_scales = [8, 16, 32],
feat_stride = 16,
mode = "training",
):
super(RegionProposalNetwork, self).__init__()
# 生成基础先验框,shape为[9, 4]
self.anchor_base = generate_anchor_base(anchor_scales = anchor_scales, ratios = ratios)
n_anchor = self.anchor_base.shape[0]
# 先进行一个3x3的卷积,可理解为特征整合
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 3, 1, 1)
# 分类预测先验框内部是否包含物体
self.score = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, n_anchor * 2, 1, 1, 0)
# 回归预测对先验框进行调整
self.loc = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, n_anchor * 4, 1, 1, 0)
# 特征点间距步长
self.feat_stride = feat_stride
# 用于对建议框解码并进行非极大抑制
self.proposal_layer = ProposalCreator(mode)
def forward(self, x, img_size, scale=1.):
n, _, h, w = x.shape
# 先进行一个3x3的卷积,可理解为特征整合
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
# 回归预测对先验框进行调整
rpn_locs = self.loc(x)
rpn_locs = rpn_locs.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(n, -1, 4)
# 分类预测先验框内部是否包含物体
rpn_scores = self.score(x)
rpn_scores = rpn_scores.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(n, -1, 2)
# 进行softmax概率计算,每个先验框只有两个判别结果
# 内部包含物体或者内部不包含物体,rpn_softmax_scores[:, :, 1]的内容为包含物体的概率
rpn_softmax_scores = F.softmax(rpn_scores, dim=-1)
rpn_fg_scores = rpn_softmax_scores[:, :, 1].contiguous()
rpn_fg_scores = rpn_fg_scores.view(n, -1)
# 生成先验框,此时获得的anchor是布满网格点的,当输入图片为600,600,3的时候,shape为(12996, 4)
anchor = _enumerate_shifted_anchor(np.array(self.anchor_base), self.feat_stride, h, w)
rois = list()
roi_indices = list()
for i in range(n):
roi = self.proposal_layer(rpn_locs[i], rpn_fg_scores[i], anchor, img_size, scale = scale)
batch_index = i * torch.ones((len(roi),))
rois.append(roi.unsqueeze(0))
roi_indices.append(batch_index.unsqueeze(0))
rois = torch.cat(rois, dim=0).type_as(x)
roi_indices = torch.cat(roi_indices, dim=0).type_as(x)
anchor = torch.from_numpy(anchor).unsqueeze(0).float().to(x.device)
return rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor
⚪ Anchor设置
anchor是人为定义的先验边界框。对于输出特征上的每个像素,以该像素对应输入图像上的像素为中心,预先设置一系列具有不同尺寸和长宽比的边界框,将其作为检测目标的候选区域。具体地,设置检测框的基础尺寸为$16$,并选定三种尺度($8,16,32$)和三种长宽比($0.5,1,2$),则每个点会设置$9$个anchor;总计在原始图像中设置$50\times 38 \times 9=17100$个anchor。注意到部分anchor的尺寸可能会超出原图尺寸(表现为负数或者超过$800/600$),因此需要进行clip操作。

# 生成基础的先验框
def generate_anchor_base(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2], anchor_scales=[8, 16, 32]):
anchor_base = np.zeros((len(ratios) * len(anchor_scales), 4), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(len(ratios)):
for j in range(len(anchor_scales)):
h = base_size * anchor_scales[j] * np.sqrt(ratios[i])
w = base_size * anchor_scales[j] * np.sqrt(1. / ratios[i])
index = i * len(anchor_scales) + j
anchor_base[index, 0] = - h / 2.
anchor_base[index, 1] = - w / 2.
anchor_base[index, 2] = h / 2.
anchor_base[index, 3] = w / 2.
return anchor_base
# 对基础先验框进行拓展对应到所有特征点上
def _enumerate_shifted_anchor(anchor_base, feat_stride=16, height=38, width=50):
# 计算网格中心点(共N个)
shift_x = np.arange(0, width * feat_stride, feat_stride)
shift_y = np.arange(0, height * feat_stride, feat_stride)
shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
shift = np.stack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(), shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(),), axis=1)
#每个网格点上的9个先验框
K = anchor_base.shape[0]
N = shift.shape[0]
anchor = anchor_base.reshape((1, K, 4)) + shift.reshape((N, 1, 4))
# 所有的先验框
anchor = anchor.reshape((N * K, 4)).astype(np.float32)
return anchor
⚪ 边界框回归
给定anchor预设的边界框坐标$p=(p_x,p_y,p_w,p_h)$及其标签$g=(g_x,g_y,g_w,g_h)$,分别代表边界框的中心位置及其宽度和高度。边界框回归旨在通过一个函数$d(\cdot)$学习中心位置的尺度不变变换以及宽度和高度的对数尺度变换:
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{g}_x &= p_wd_x(p) + p_x \\ \hat{g}_y &= p_hd_y(p) + p_y \\ \hat{g}_w &= p_w \exp(d_w(p)) \\ \hat{g}_h &= p_h \exp(d_h(p)) \end{aligned}\]
通过采用上述变换,回归器的输出\(d_i(p),i\in \{x,y,w,h\}\)取值范围为$(-\infty,+\infty)$。回归器学习的目标为:
\[\begin{aligned} t_x &= (g_x-p_x)/p_w \\ t_y &= (g_y-p_y)/p_h \\ t_w &= \log (g_w/p_w) \\ t_h &= \log (g_h/p_h) \\ \end{aligned}\]def loc2bbox(anchor, loc):
if anchor.size()[0] == 0:
return torch.zeros((0, 4), dtype=loc.dtype)
src_width = torch.unsqueeze(anchor[:, 2] - anchor[:, 0], -1)
src_height = torch.unsqueeze(anchor[:, 3] - anchor[:, 1], -1)
src_ctr_x = torch.unsqueeze(anchor[:, 0], -1) + 0.5 * src_width
src_ctr_y = torch.unsqueeze(anchor[:, 1], -1) + 0.5 * src_height
tx = loc[:, 0::4]
ty = loc[:, 1::4]
tw = loc[:, 2::4]
th = loc[:, 3::4]
ctr_x = tx * src_width + src_ctr_x
ctr_y = ty * src_height + src_ctr_y
w = torch.exp(tw) * src_width
h = torch.exp(th) * src_height
corrected_bbox = torch.zeros_like(loc)
corrected_bbox[:, 0::4] = ctr_x - 0.5 * w
corrected_bbox[:, 1::4] = ctr_y - 0.5 * h
corrected_bbox[:, 2::4] = ctr_x + 0.5 * w
corrected_bbox[:, 3::4] = ctr_y + 0.5 * h
return corrected_bbox
⚪ Proposal Layer
Proposal Layer接收RPN的输出(anchor类别+边界框偏移量),计算位置修正后的positive anchor,并将其投影到卷积网络的特征映射上,提取proposals。
Proposal Layer提取proposals的前向过程如下:
- 根据RPN的输出边界框偏移量($t_x,t_y,t_w,t_h$)对anchor进行边界框回归;
- 对所有anchor按照RPN的输出正类类别得分由大到小排序,提取前$N=6000$个anchor,即提取修正位置后的positive anchors;
- 限定超出图像边界的positive anchors为图像边界;
- 剔除尺寸非常小($\leq 16$)的positive anchors;
- 对剩余的positive anchors进行非极大值抑制;
- 最终剩余的positive anchors作为proposals结果(对应输入图像中的边界框)。
from torchvision.ops import nms
class ProposalCreator():
def __init__(
self,
mode,
nms_iou = 0.7,
n_train_pre_nms = 12000,
n_train_post_nms = 600,
n_test_pre_nms = 3000,
n_test_post_nms = 300,
min_size = 16
):
# 设置预测还是训练
self.mode = mode
# 建议框非极大抑制的iou大小
self.nms_iou = nms_iou
# 训练用到的建议框数量
self.n_train_pre_nms = n_train_pre_nms
self.n_train_post_nms = n_train_post_nms
# 预测用到的建议框数量
self.n_test_pre_nms = n_test_pre_nms
self.n_test_post_nms = n_test_post_nms
self.min_size = min_size
def __call__(self, loc, score, anchor, img_size, scale=1.):
if self.mode == "training":
n_pre_nms = self.n_train_pre_nms
n_post_nms = self.n_train_post_nms
else:
n_pre_nms = self.n_test_pre_nms
n_post_nms = self.n_test_post_nms
# 将先验框转换成tensor
anchor = torch.from_numpy(anchor).type_as(loc)
# 将RPN网络预测结果转化成建议框
roi = loc2bbox(anchor, loc)
# 防止建议框超出图像边缘
roi[:, [0, 2]] = torch.clamp(roi[:, [0, 2]], min = 0, max = img_size[1])
roi[:, [1, 3]] = torch.clamp(roi[:, [1, 3]], min = 0, max = img_size[0])
# 建议框的宽高的最小值不可以小于16
min_size = self.min_size * scale
keep = torch.where(((roi[:, 2] - roi[:, 0]) >= min_size) & ((roi[:, 3] - roi[:, 1]) >= min_size))[0]
# 将对应的建议框保留下来
roi = roi[keep, :]
score = score[keep]
# 根据得分进行排序,取出建议框
order = torch.argsort(score, descending=True)
if n_pre_nms > 0:
order = order[:n_pre_nms]
roi = roi[order, :]
score = score[order]
# 对建议框进行非极大抑制
keep = nms(roi, score, self.nms_iou)
if len(keep) < n_post_nms:
index_extra = np.random.choice(range(len(keep)), size=(n_post_nms - len(keep)), replace=True)
keep = torch.cat([keep, keep[index_extra]])
keep = keep[:n_post_nms]
roi = roi[keep]
return roi
(3)RoI Pooling
RoI Pooling是一种最大池化层,它把图像特征映射中的任意尺寸$H\times W$的区域映射为固定尺寸$h\times w$的特征。在实现时把输入区域划分为$H\times W$的窗口,

RoI Pooling层接收Proposal Layer输出的proposal。由于anchor是在原始图像尺度上设置的,因此通过下采样率$16$把proposal映射到特征映射尺度。再将每个proposal对应的特征映射区域划分为固定尺寸($7 \times 7$)的网格;对网格的每一份都进行最大池化处理。RoI Pooling层的输出是固定尺寸($256\times 7 \times 7$)的特征。
# RoI Pooling的函数调用
from torchvision.ops import roi_pool
fp = torch.randn([1, 1, 5, 5]) # [b, c, h, w]
boxes = torch.tensor([[0, 0, 0, 1, 1]]).float() # [batch_id, x1, y1, x2, y2]
pooled_features = roi_pool(fp, boxes, [4, 4])
# RoI Pooling的类调用
from torchvision.ops import RoIPool
self.roi = RoIPool((roi_size, roi_size), spatial_scale)
pool = self.roi(x, indices_and_rois)
(4)分类与回归Head
从RoI Pooling获取到$256\times 7 \times 7$大小的proposal feature maps后,送入后续网络:
- 通过全连接层和softmax对proposals进行分类;
- 对proposals进行边界框回归,获取更高精度的检测框。
class VGG16RoIHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_class, roi_size, spatial_scale, classifier):
super(VGG16RoIHead, self).__init__()
self.classifier = classifier
# 对ROIPooling后的的结果进行回归预测
self.cls_loc = nn.Linear(4096, n_class * 4)
# 对ROIPooling后的的结果进行分类
self.score = nn.Linear(4096, n_class)
self.roi = RoIPool((roi_size, roi_size), spatial_scale)
def forward(self, x, rois, roi_indices, img_size):
n, _, _, _ = x.shape
if x.is_cuda:
roi_indices = roi_indices.cuda()
rois = rois.cuda()
rois = torch.flatten(rois, 0, 1)
roi_indices = torch.flatten(roi_indices, 0, 1)
rois_feature_map = torch.zeros_like(rois)
rois_feature_map[:, [0,2]] = rois[:, [0,2]] / img_size[1] * x.size()[3]
rois_feature_map[:, [1,3]] = rois[:, [1,3]] / img_size[0] * x.size()[2]
indices_and_rois = torch.cat([roi_indices[:, None], rois_feature_map], dim=1)
# 利用建议框对公用特征层进行截取
pool = self.roi(x, indices_and_rois)
# 利用classifier网络进行特征提取
pool = pool.view(pool.size(0), -1)
# 当输入为一张图片的时候,这里获得的f7的shape为[300, 4096]
fc7 = self.classifier(pool)
roi_cls_locs = self.cls_loc(fc7)
roi_scores = self.score(fc7)
roi_cls_locs = roi_cls_locs.view(n, -1, roi_cls_locs.size(1))
roi_scores = roi_scores.view(n, -1, roi_scores.size(1))
return roi_cls_locs, roi_scores
(5)Faster R-CNN的完整实现
Faster R-CNN模型的整体结构设置如下:
class FasterRCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes,
mode = "training",
feat_stride = 16,
anchor_scales = [8, 16, 32],
ratios = [0.5, 1, 2],
pretrained = False):
super(FasterRCNN, self).__init__()
self.feat_stride = feat_stride
self.extractor, classifier = decom_vgg16(pretrained)
self.rpn = RegionProposalNetwork(
512, 512,
ratios = ratios,
anchor_scales = anchor_scales,
feat_stride = self.feat_stride,
mode = mode
)
self.head = VGG16RoIHead(
n_class = num_classes + 1,
roi_size = 7,
spatial_scale = 1,
classifier = classifier
)
def forward(self, x, scale=1., mode="forward"):
if mode == "forward":
# 获得网络的分类结果和回归结果
img_size = x.shape[2:]
base_feature = self.extractor.forward(x)
_, _, rois, roi_indices, _ = self.rpn.forward(base_feature, img_size, scale)
roi_cls_locs, roi_scores = self.head.forward(base_feature, rois, roi_indices, img_size)
return roi_cls_locs, roi_scores, rois, roi_indices
elif mode == "extractor":
# 利用主干网络提取特征
base_feature = self.extractor.forward(x)
return base_feature
elif mode == "rpn":
base_feature, img_size = x
# 获得建议框
rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor = self.rpn.forward(base_feature, img_size, scale)
return rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor
elif mode == "head":
base_feature, rois, roi_indices, img_size = x
# 获得classifier的分类结果和回归结果
roi_cls_locs, roi_scores = self.head.forward(base_feature, rois, roi_indices, img_size)
return roi_cls_locs, roi_scores
2. Faster RCNN的训练过程
在原论文中,Faster R-CNN模型的训练过程如下:
- 使用预训练的卷积网络提取特征映射,训练RPN网络;
- 使用训练好的RPN网络收集proposals;
- 根据proposals第一次训练Faster R-CNN模型;
- 第二次训练RPN网络;
- 使用训练好的RPN网络收集proposals;
- 第二次训练Faster R-CNN模型。
受当时硬件和开发环境限制,Faster R-CNN模型采用上述分步训练过程,以缓解训练过程中的优化困难。如今Pytorch等开发环境已经相当成熟,因此Faster R-CNN模型可以直接进行端到端训练。
⚪ 损失函数
Faster R-CNN模型的损失函数包括RPN的分类与回归损失和网络输出的分类与回归损失。
RPN的输出包括两个部分:每个anchor的正类别概率\(\hat{p}_i\)和正类别anchor的预测边界框偏移量\(\hat{t}_i\)。类别标签$p$通过计算对应anchor与ground truth之间的IoU区分:IoU$>0.7$视为正类;IoU$<0.3$视为负类;其余anchor丢弃。
def bbox_iou(bbox_a, bbox_b):
if bbox_a.shape[1] != 4 or bbox_b.shape[1] != 4:
print(bbox_a, bbox_b)
raise IndexError
tl = np.maximum(bbox_a[:, None, :2], bbox_b[:, :2])
br = np.minimum(bbox_a[:, None, 2:], bbox_b[:, 2:])
area_i = np.prod(br - tl, axis=2) * (tl < br).all(axis=2)
area_a = np.prod(bbox_a[:, 2:] - bbox_a[:, :2], axis=1)
area_b = np.prod(bbox_b[:, 2:] - bbox_b[:, :2], axis=1)
return area_i / (area_a[:, None] + area_b - area_i)
def bbox2loc(src_bbox, dst_bbox):
width = src_bbox[:, 2] - src_bbox[:, 0]
height = src_bbox[:, 3] - src_bbox[:, 1]
ctr_x = src_bbox[:, 0] + 0.5 * width
ctr_y = src_bbox[:, 1] + 0.5 * height
base_width = dst_bbox[:, 2] - dst_bbox[:, 0]
base_height = dst_bbox[:, 3] - dst_bbox[:, 1]
base_ctr_x = dst_bbox[:, 0] + 0.5 * base_width
base_ctr_y = dst_bbox[:, 1] + 0.5 * base_height
eps = np.finfo(height.dtype).eps
width = np.maximum(width, eps)
height = np.maximum(height, eps)
dx = (base_ctr_x - ctr_x) / width
dy = (base_ctr_y - ctr_y) / height
dw = np.log(base_width / width)
dh = np.log(base_height / height)
loc = np.vstack((dx, dy, dw, dh)).transpose()
return loc
class AnchorTargetCreator(object):
def __init__(self, n_sample=256, pos_iou_thresh=0.7, neg_iou_thresh=0.3, pos_ratio=0.5):
self.n_sample = n_sample
self.pos_iou_thresh = pos_iou_thresh
self.neg_iou_thresh = neg_iou_thresh
self.pos_ratio = pos_ratio
def __call__(self, bbox, anchor):
argmax_ious, label = self._create_label(anchor, bbox)
if (label > 0).any():
loc = bbox2loc(anchor, bbox[argmax_ious])
return loc, label
else:
return np.zeros_like(anchor), label
def _calc_ious(self, anchor, bbox):
# anchor和bbox的iou
# 获得的ious的shape为[num_anchors, num_gt]
ious = bbox_iou(anchor, bbox)
if len(bbox)==0:
return np.zeros(len(anchor), np.int32), np.zeros(len(anchor)), np.zeros(len(bbox))
# 获得每一个先验框最对应的真实框 [num_anchors, ]
argmax_ious = ious.argmax(axis=1)
# 找出每一个先验框最对应的真实框的iou [num_anchors, ]
max_ious = np.max(ious, axis=1)
# 获得每一个真实框最对应的先验框 [num_gt, ]
gt_argmax_ious = ious.argmax(axis=0)
# 保证每一个真实框都存在对应的先验框
for i in range(len(gt_argmax_ious)):
argmax_ious[gt_argmax_ious[i]] = i
return argmax_ious, max_ious, gt_argmax_ious
def _create_label(self, anchor, bbox):
# 1是正样本,0是负样本,-1忽略
# 初始化的时候全部设置为-1
label = np.empty((len(anchor),), dtype=np.int32)
label.fill(-1)
# argmax_ious为每个先验框对应的最大的真实框的序号 [num_anchors, ]
# max_ious为每个先验框对应的最大的真实框的iou [num_anchors, ]
# gt_argmax_ious为每个真实框对应的最大的先验框的序号 [num_gt, ]
argmax_ious, max_ious, gt_argmax_ious = self._calc_ious(anchor, bbox)
# 如果小于门限值则设置为负样本
# 如果大于门限值则设置为正样本
# 每个真实框至少对应一个先验框
label[max_ious < self.neg_iou_thresh] = 0
label[max_ious >= self.pos_iou_thresh] = 1
if len(gt_argmax_ious)>0:
label[gt_argmax_ious] = 1
# 判断正样本数量是否大于128,如果大于则限制在128
n_pos = int(self.pos_ratio * self.n_sample)
pos_index = np.where(label == 1)[0]
if len(pos_index) > n_pos:
disable_index = np.random.choice(pos_index, size=(len(pos_index) - n_pos), replace=False)
label[disable_index] = -1
# 平衡正负样本,保持总数量为256
n_neg = self.n_sample - np.sum(label == 1)
neg_index = np.where(label == 0)[0]
if len(neg_index) > n_neg:
disable_index = np.random.choice(neg_index, size=(len(neg_index) - n_neg), replace=False)
label[disable_index] = -1
return argmax_ious, label
RPN的总损失函数为:
\[\begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}_{RPN}(\hat{p},p,\hat{t},t)&=\frac{1}{N_{cls}}\sum_i\mathcal{L}_{cls}(\hat{p}_i,p_i)+\frac{\lambda}{N_{reg}}\sum_ip_i\mathcal{L}_{reg}(\hat{t}_i,t_i) \\ \mathcal{L}_{cls}(\hat{p},p) &= -p\log \hat{p}-(1-p) \log(1-\hat{p}) \\ \mathcal{L}_{reg}(\hat{t},t) &= \sum_{j \in \{x,y,w,h\}}L_1^{smooth}(\hat{t}-t) \end{aligned}\]其中边界框回归损失采用平滑L1损失,这是一种鲁棒的损失函数,对离群点不敏感:
\[L_1^{smooth}(x) = \begin{cases} 0.5x^2, & |x| < 1 \\ |x| - 0.5, & |x| \geq 1 \end{cases}\]
网络整体的输出包括两个部分:每个proposal的预测类别概率分布$p=(p_0,…,p_K)$和标签类别$c$ ($0$表示背景类),则总损失函数为:
\[\begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}(p,c,\hat{t},t)&=\mathcal{L}_{cls}(p,c)+\mathbb{I}(c \neq 0)\mathcal{L}_{box}(\hat{t},t) \\ \mathcal{L}_{cls}(p,c) &= -\log p_c \\ \mathcal{L}_{box}(\hat{t},t) &= \sum_{i \in \{x,y,w,h\}}L_1^{smooth}(\hat{t}-t) \end{aligned}\]class ProposalTargetCreator(object):
def __init__(self, n_sample=128, pos_ratio=0.5, pos_iou_thresh=0.5, neg_iou_thresh_high=0.5, neg_iou_thresh_low=0):
self.n_sample = n_sample
self.pos_ratio = pos_ratio
self.pos_roi_per_image = np.round(self.n_sample * self.pos_ratio)
self.pos_iou_thresh = pos_iou_thresh
self.neg_iou_thresh_high = neg_iou_thresh_high
self.neg_iou_thresh_low = neg_iou_thresh_low
def __call__(self, roi, bbox, label, loc_normalize_std=(0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2)):
roi = np.concatenate((roi.detach().cpu().numpy(), bbox), axis=0)
# 计算建议框和真实框的重合程度
iou = bbox_iou(roi, bbox)
if len(bbox)==0:
gt_assignment = np.zeros(len(roi), np.int32)
max_iou = np.zeros(len(roi))
gt_roi_label = np.zeros(len(roi))
else:
# 获得每一个建议框最对应的真实框 [num_roi, ]
gt_assignment = iou.argmax(axis=1)
# 获得每一个建议框最对应的真实框的iou [num_roi, ]
max_iou = iou.max(axis=1)
# 真实框的标签要+1因为有背景的存在
gt_roi_label = label[gt_assignment] + 1
# 满足建议框和真实框重合程度大于pos_iou_thresh的作为正样本
# 将正样本的数量限制在self.pos_roi_per_image以内
pos_index = np.where(max_iou >= self.pos_iou_thresh)[0]
pos_roi_per_this_image = int(min(self.pos_roi_per_image, pos_index.size))
if pos_index.size > 0:
pos_index = np.random.choice(pos_index, size=pos_roi_per_this_image, replace=False)
# 满足建议框和真实框重合程度小于neg_iou_thresh_high大于neg_iou_thresh_low作为负样本
# 将正样本的数量和负样本的数量的总和固定成self.n_sample
neg_index = np.where((max_iou < self.neg_iou_thresh_high) & (max_iou >= self.neg_iou_thresh_low))[0]
neg_roi_per_this_image = self.n_sample - pos_roi_per_this_image
neg_roi_per_this_image = int(min(neg_roi_per_this_image, neg_index.size))
if neg_index.size > 0:
neg_index = np.random.choice(neg_index, size=neg_roi_per_this_image, replace=False)
keep_index = np.append(pos_index, neg_index)
sample_roi = roi[keep_index] # [n_sample, ]
if len(bbox)==0:
return sample_roi, np.zeros_like(sample_roi), gt_roi_label[keep_index]
gt_roi_loc = bbox2loc(sample_roi, bbox[gt_assignment[keep_index]])
gt_roi_loc = (gt_roi_loc / np.array(loc_normalize_std, np.float32)) # [n_sample, 4]
gt_roi_label = gt_roi_label[keep_index] # [n_sample, ]
gt_roi_label[pos_roi_per_this_image:] = 0
return sample_roi, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label
⚪ 训练过程
class FasterRCNNTrainer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model_train, optimizer):
super(FasterRCNNTrainer, self).__init__()
self.model_train = model_train
self.optimizer = optimizer
self.rpn_sigma = 1
self.roi_sigma = 1
self.anchor_target_creator = AnchorTargetCreator()
self.proposal_target_creator = ProposalTargetCreator()
self.loc_normalize_std = [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]
# smooth L1 loss
def _fast_rcnn_loc_loss(self, pred_loc, gt_loc, gt_label, sigma):
pred_loc = pred_loc[gt_label > 0]
gt_loc = gt_loc[gt_label > 0]
sigma_squared = sigma ** 2
regression_diff = (gt_loc - pred_loc)
regression_diff = regression_diff.abs().float()
regression_loss = torch.where(
regression_diff < (1. / sigma_squared),
0.5 * sigma_squared * regression_diff ** 2,
regression_diff - 0.5 / sigma_squared
)
regression_loss = regression_loss.sum()
num_pos = (gt_label > 0).sum().float()
regression_loss /= torch.max(num_pos, torch.ones_like(num_pos))
return regression_loss
def forward(self, imgs, bboxes, labels, scale):
n = imgs.shape[0]
img_size = imgs.shape[2:]
#-------------------------------#
# 获取公用特征层
#-------------------------------#
base_feature = self.model_train(imgs, mode = 'extractor')
# -------------------------------------------------- #
# 利用rpn网络获得调整参数、得分、建议框、先验框
# -------------------------------------------------- #
rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor = self.model_train(x = [base_feature, img_size], scale = scale, mode = 'rpn')
rpn_loc_loss_all, rpn_cls_loss_all, roi_loc_loss_all, roi_cls_loss_all = 0, 0, 0, 0
sample_rois, sample_indexes, gt_roi_locs, gt_roi_labels = [], [], [], []
for i in range(n):
bbox = bboxes[i]
label = labels[i]
rpn_loc = rpn_locs[i]
rpn_score = rpn_scores[i]
roi = rois[i]
# -------------------------------------------------- #
# 利用真实框和先验框获得建议框网络应该有的预测结果
# 给每个先验框都打上标签
# gt_rpn_loc [num_anchors, 4]
# gt_rpn_label [num_anchors, ]
# -------------------------------------------------- #
gt_rpn_loc, gt_rpn_label = self.anchor_target_creator(bbox, anchor[0].cpu().numpy())
gt_rpn_loc = torch.Tensor(gt_rpn_loc).type_as(rpn_locs)
gt_rpn_label = torch.Tensor(gt_rpn_label).type_as(rpn_locs).long()
# -------------------------------------------------- #
# 分别计算建议框网络的回归损失和分类损失
# -------------------------------------------------- #
rpn_loc_loss = self._fast_rcnn_loc_loss(rpn_loc, gt_rpn_loc, gt_rpn_label, self.rpn_sigma)
rpn_cls_loss = F.cross_entropy(rpn_score, gt_rpn_label, ignore_index=-1)
rpn_loc_loss_all += rpn_loc_loss
rpn_cls_loss_all += rpn_cls_loss
# ------------------------------------------------------ #
# 利用真实框和建议框获得classifier网络应该有的预测结果
# 获得三个变量,分别是sample_roi, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label
# sample_roi [n_sample, ]
# gt_roi_loc [n_sample, 4]
# gt_roi_label [n_sample, ]
# ------------------------------------------------------ #
sample_roi, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label = self.proposal_target_creator(roi, bbox, label, self.loc_normalize_std)
sample_rois.append(torch.Tensor(sample_roi).type_as(rpn_locs))
sample_indexes.append(torch.ones(len(sample_roi)).type_as(rpn_locs) * roi_indices[i][0])
gt_roi_locs.append(torch.Tensor(gt_roi_loc).type_as(rpn_locs))
gt_roi_labels.append(torch.Tensor(gt_roi_label).type_as(rpn_locs).long())
sample_rois = torch.stack(sample_rois, dim=0)
sample_indexes = torch.stack(sample_indexes, dim=0)
roi_cls_locs, roi_scores = self.model_train([base_feature, sample_rois, sample_indexes, img_size], mode = 'head')
for i in range(n):
# ------------------------------------------------------ #
# 根据建议框的种类,取出对应的回归预测结果
# ------------------------------------------------------ #
n_sample = roi_cls_locs.size()[1]
roi_cls_loc = roi_cls_locs[i]
roi_score = roi_scores[i]
gt_roi_loc = gt_roi_locs[i]
gt_roi_label = gt_roi_labels[i]
roi_cls_loc = roi_cls_loc.view(n_sample, -1, 4)
roi_loc = roi_cls_loc[torch.arange(0, n_sample), gt_roi_label]
# -------------------------------------------------- #
# 分别计算Classifier网络的回归损失和分类损失
# -------------------------------------------------- #
roi_loc_loss = self._fast_rcnn_loc_loss(roi_loc, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label.data, self.roi_sigma)
roi_cls_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(roi_score, gt_roi_label)
roi_loc_loss_all += roi_loc_loss
roi_cls_loss_all += roi_cls_loss
losses = [rpn_loc_loss_all/n, rpn_cls_loss_all/n, roi_loc_loss_all/n, roi_cls_loss_all/n]
losses = losses + [sum(losses)]
return losses
def train_step(self, imgs, bboxes, labels, scale):
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
losses = self.forward(imgs, bboxes, labels, scale)
losses[-1].backward()
self.optimizer.step()
return losses
Faster RCNN的完整PyTorch实现可参考 faster-rcnn-pytorch。


