A^2-Net:双重注意力网络.
本文的核心想法:首先使用二阶注意力池化将整幅图的所有关键的特征搜集到一个集合里,然后用一种注意力机制将这些特征分配给图像的每个位置。
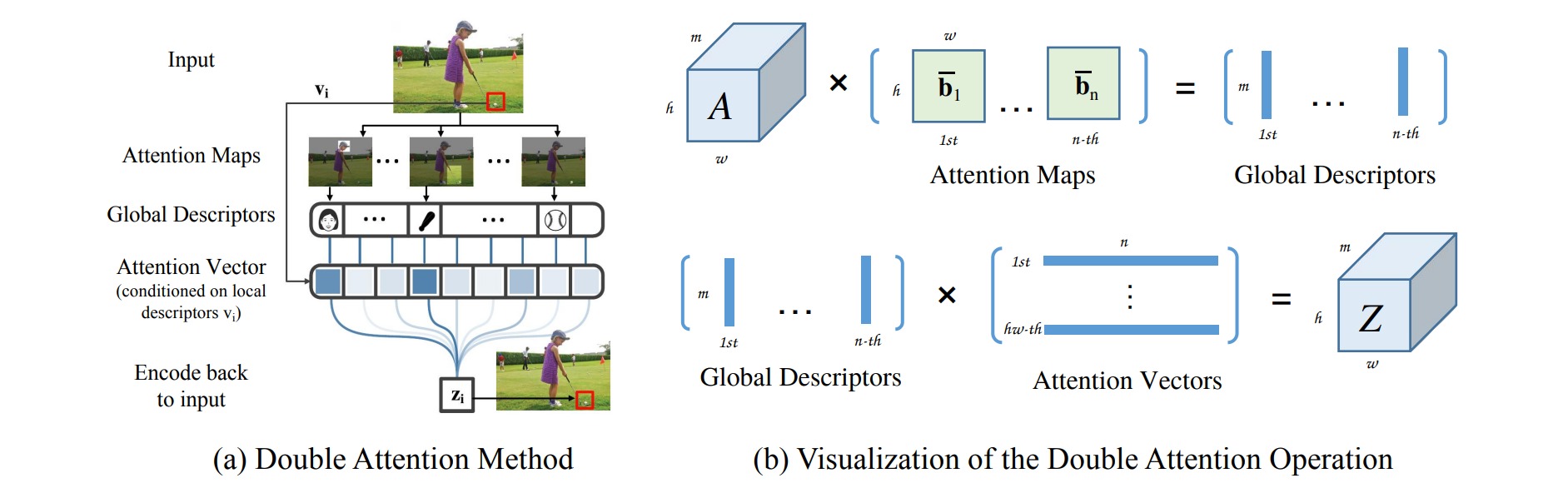
模型首先会计算出一系列global descriptors,然后每个特征位置会根据自己本身的特征来计算对每个global descriptor的权重,从而能对自己的特征做一个补充,比如图上的红框处是一个baseball,所以它对baseball的权重就小,对其他的权重就大一些。
得到所有位置的attention vectors之后,组成的矩阵与global descriptors相乘便恢复到最开始的大小,写成数学形式如下,其中$i$代表特征位置:
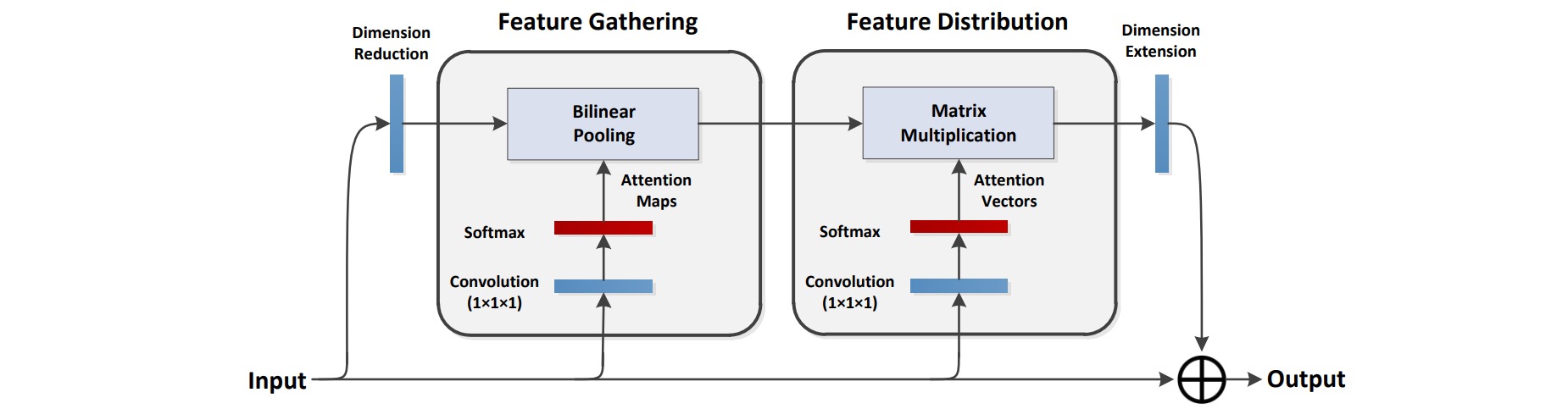
\[z_i = F_{distr}(G_{gather}(X),v_i)\]⚪ Feature Gathering
Feature Gathering的目的是从输入特征中提取global descriptors,实现过程是使用两个卷积网络,将得到的特征做外积,从而捕捉到特征中的二阶统计规律。
假设两个卷积网络提取的特征分别为$A \in R^{m \times hw},B \in R^{n \times hw}$,则外积对应双线性池化(bilinear pooling):
\[G_{bilinear}(A,B) = A\cdot softmax(B)^T \in R^{m \times n}\]$g_i$就相当于$A$乘上一个注意力分布 $b_i$然后求和,$G$可以看做图片上视觉元素的集合。
⚪ Feature Distribution
Feature Distribution的目的是将从整幅图得到的global features分给每一个特征位置:
\[z_i = G_{gather}(X)v_i\]其中$z_i$是将$n$个global features加权得到的新的位置$i$的特征。$v_i$是每个位置$i$的attention vector,是通过$1\times 1$的卷积产生的。
⚪ Double Attention Block
结合上面的两步可以得到double attention block:
class DoubleAtten(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c):
"""
:param
in_c: 进行注意力refine的特征图的通道数目;
"""
super(DoubleAtten,self).__init__()
self.in_c = in_c
"""
以下对同一输入特征图进行卷积,产生三个尺度相同的特征图,即为文中提到A, B, V
"""
self.convA = nn.Conv2D(in_c, in_c, kernel_size=1)
self.convB = nn.Conv2D(in_c, in_c, kernel_size=1)
self.convV = nn.Conv2D(in_c, in_c, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, input):
feature_maps = self.convA(input)
atten_map = self.convB(input)
b, _, h, w = feature_maps.shape
feature_maps = feature_maps.view([b, 1, self.in_c, h*w]) # 对 A 进行reshape
atten_map = atten_map.view([b, self.in_c, 1, h*w]) # 对 B 进行reshape 生成 attention_aps
global_descriptors = torch.mean((feature_maps * F.softmax(atten_map, axis=-1)),axis=-1) # 特征图与attention_maps 相乘生成全局特征描述子
v = self.convV(input)
atten_vectors = F.softmax(v.view([b, self.in_c, h*w]), axis=-1) # 生成 attention_vectors
out = torch.bmm(atten_vectors.transpose([0,2,1]), global_descriptors).transpose([0,2,1]) # 注意力向量左乘全局特征描述子
return out.view(b, -1, h, w)


