SKNet:通过注意力机制实现卷积核尺寸选择.
SKNet首先同时使用不同大小的卷积核($3 \times 3$, $5 \times 5$, $7 \times 7$…)作为不同的分支提取特征,然后通过通道注意力机制融合这些特征,最终融合了不同尺寸的卷积核对应的感受野的信息。
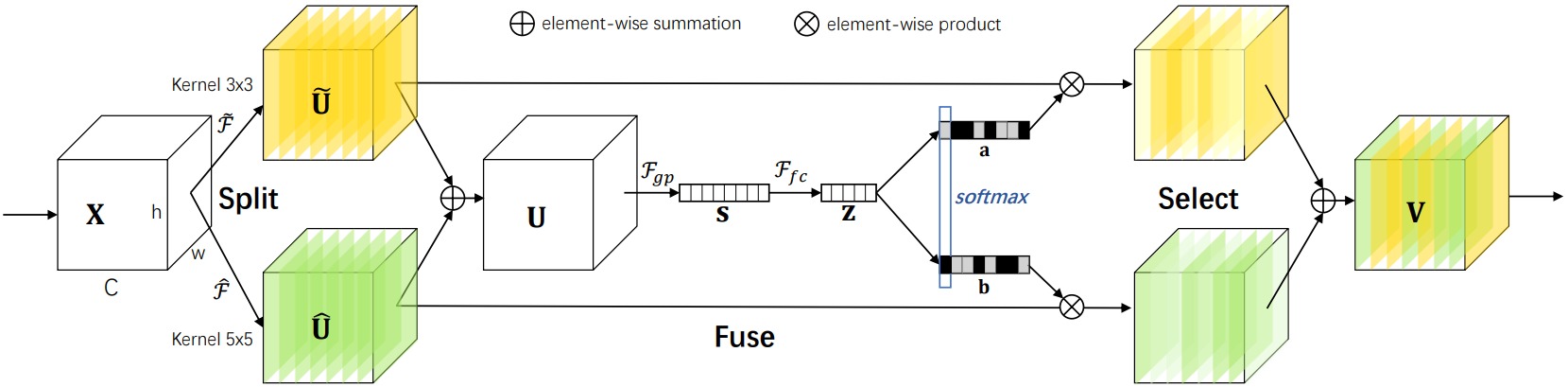
上图给出了$2$个分支的SKNet模块,把每个分支的特征求和后通过带瓶颈层的全连接层映射为一组权重,权重的对应位置使用Softmax函数进行归一化,然后分别与每个分支的特征相乘后相加作为输出特征。
Pytorch代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SKLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, M, r, L=32):
super(SKLayer, self).__init__()
""" Constructor
Args:
features: input channel dimensionality.
M: the number of branchs.
r: the radio for compute d, the length of z.
L: the minimum dim of the vector z in paper, default 32.
"""
d = max(int(features / r), L)
self.M = M
self.features = features
self.convs = nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(M):
self.convs.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(features,
features,
kernel_size=3 + i * 2,
stride=1,
padding=1 + i),
nn.BatchNorm2d(features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False)))
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(features, d)
self.fcs = nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(M):
self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(d, features))
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
for i, conv in enumerate(self.convs):
fea = conv(x).unsqueeze_(dim=1) # [B, 1, C, H, W]
if i == 0:
feas = fea
else:
feas = torch.cat([feas, fea], dim=1) # [B, M, C, H, W]
fea_U = torch.sum(feas, dim=1) # [B, C, H, W]
fea_s = self.avgpool(fea_U).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1) # [B, C]
fea_z = self.fc(fea_s) # [B, C/r]
for i, fc in enumerate(self.fcs):
vector = fc(fea_z).unsqueeze_(dim=1) # [B, 1, C]
if i == 0:
attention_vectors = vector
else:
attention_vectors = torch.cat([attention_vectors, vector],
dim=1) # [B, M, C]
attention_vectors = self.softmax(attention_vectors) # [B, M, C]
attention_vectors = attention_vectors.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) # [B, M, C, 1, 1]
fea_v = (feas * attention_vectors).sum(dim=1) # [B, C, H, W]
return fea_v
if __name__ == "__main__":
t = torch.ones((32, 256, 24, 24))
sk = SKLayer(256,M=2,r=2)
out = sk(t)
print(out.shape)


