SRResnet/SRGAN:使用生成对抗网络进行图像超分辨率.
直接使用MSE损失函数训练的超分辨率模型,在PSNR和SSIM等评价指标上能够得到较高的结果,但图像细节显示依旧较差。作者利用生成对抗网络的方法得到视觉特性较好的结果。

如上图所示,在图像空间中存在若干结构相似的图像,使用MSE损失将会生成这些图像的平均值,忽略图像的细节;而使用GAN的方法则会接近某张真实图像,从而保留较好的真实表现。
本文的主要贡献在于:
- 建立了使用PSNR和SSIM为评价标准的SRResNet,对图像放大$4$倍,取得了最好的测试结果;
- 提出了SRGAN网络,该网络结构根据对抗网络网络结构提出了一种新的感知损失函数(perceptual loss),利用VGG的网络特征作为内容损失函数(content loss),代替了之前的MSE损失函数。
- 对生成的图像进行MOS(mean opinion score)评价。
1. 模型结构
(1)生成器
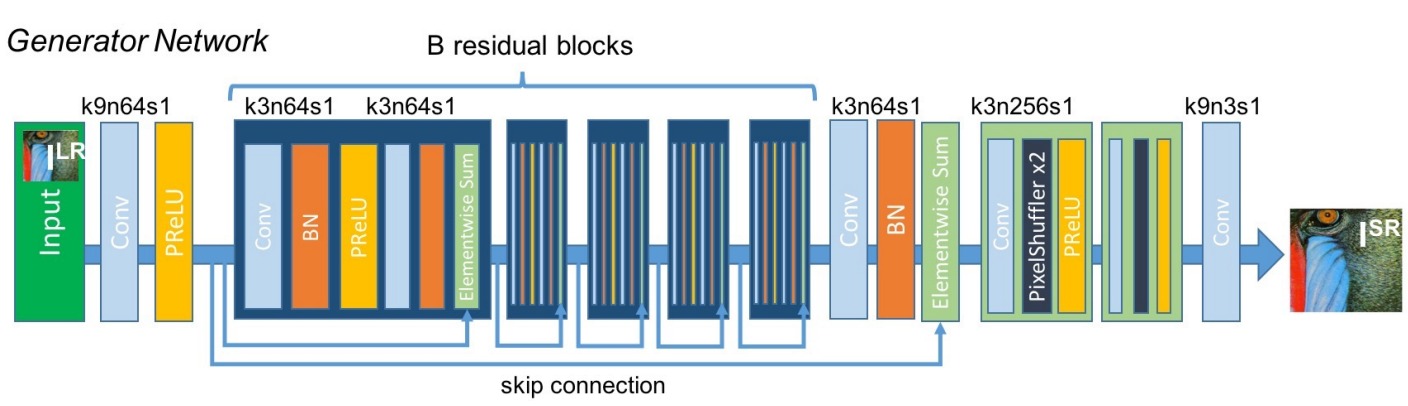
生成器结构参考了ResNet,输入低分辨率图像得到高分辨率图像,这一部分可作为SRResNet单独使用。
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_features, in_features, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_features, 0.8),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_features, in_features, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_features, 0.8),
)
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.conv_block(x)
class GeneratorResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=3, out_channels=3, n_residual_blocks=16):
super(GeneratorResNet, self).__init__()
# First layer
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=9, stride=1, padding=4), nn.PReLU())
# Residual blocks
res_blocks = []
for _ in range(n_residual_blocks):
res_blocks.append(ResidualBlock(64))
self.res_blocks = nn.Sequential(*res_blocks)
# Second conv layer post residual blocks
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1), nn.BatchNorm2d(64, 0.8))
# Upsampling layers
upsampling = []
for out_features in range(2):
upsampling += [
# nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.PixelShuffle(upscale_factor=2),
nn.PReLU(),
]
self.upsampling = nn.Sequential(*upsampling)
# Final output layer
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(64, out_channels, kernel_size=9, stride=1, padding=4), nn.Tanh())
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.conv1(x)
out = self.res_blocks(out1)
out2 = self.conv2(out)
out = torch.add(out1, out2)
out = self.upsampling(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
return out
(2)判别器
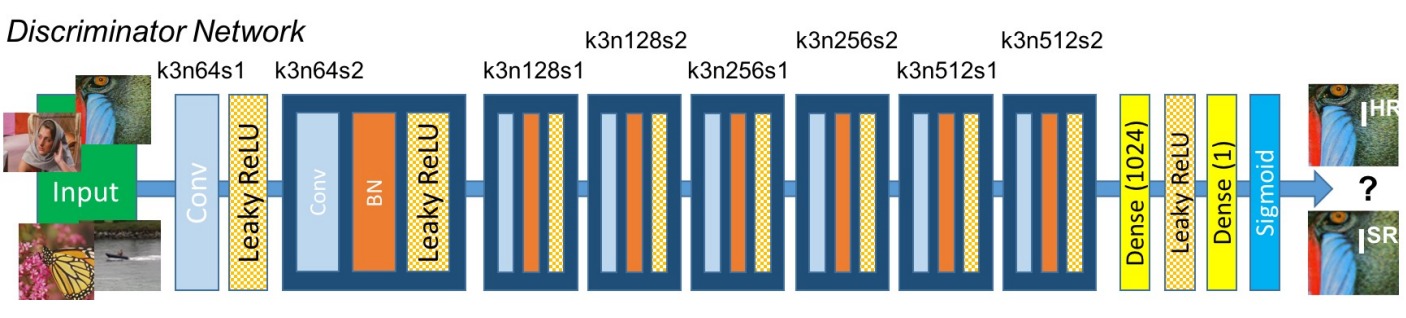
判别器结构参考了VGGNet,输入真实图像和生成的高分辨率图像,对二者进行分类。
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.input_shape = input_shape
in_channels, in_height, in_width = self.input_shape
patch_h, patch_w = int(in_height / 2 ** 4), int(in_width / 2 ** 4)
def discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, first_block=False):
layers = []
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_filters, out_filters, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1))
if not first_block:
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_filters))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(out_filters, out_filters, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_filters))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
layers = []
in_filters = in_channels
for i, out_filters in enumerate([64, 128, 256, 512]):
layers.extend(discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, first_block=(i == 0)))
in_filters = out_filters
layers.append(nn.Linear(512*patch_h*patch_w, 1024), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), nn.Linear(1024, 1), nn.Tanh())
self.model = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, img):
return self.model(img)
2. 损失函数
为了训练SRGAN,作者提出了感知损失函数(perceptual loss)$l^{SR}$,由内容损失函数(content loss)$l_X^{SR}$和对抗损失函数(adversarial loss)$l_{Gen}^{SR}$组成。

内容损失函数(content loss)$l_X^{SR}$基于一个预训练的VGG19网络,通过比较生成图像和真实图像的网络中特征差异进行定义。其中$Φ_{i,j}$表示VGG19网络中第$i$个池化层之前的第$j$个卷积层(在激活函数之后)的特征图。
from torchvision.models import vgg19
class FeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
vgg19_model = vgg19(pretrained=True)
self.feature_extractor = nn.Sequential(*list(vgg19_model.features.children())[:18])
def forward(self, img):
return self.feature_extractor(img)
feature_extractor = FeatureExtractor()
feature_extractor.eval()
criterion_content = torch.nn.L1Loss()
# Content loss
gen_features = feature_extractor(gen_hr)
real_features = feature_extractor(imgs_hr)
loss_content = criterion_content(gen_features, real_features.detach())
对抗损失函数(adversarial loss)$l_{Gen}^{SR}$试图使判别器无法正确的分类生成器获得的结果, 训练按照生成对抗网络的损失进行:
\[\mathop{\min}_{θ_G} \mathop{\max}_{θ_D} E_{I^{HR} \text{~} p_{train}(I^{HR})}[logD_{θ_D}(I^{HR})] + E_{I^{LR} \text{~} p_{G}(I^{LR})}[log(1-D_{θ_D}(G_{θ_G}(I^{LR})))]\]generator = GeneratorResNet()
discriminator = Discriminator()
adversarial_loss = torch.nn.BCELoss()
# 定义优化器
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=0.0002, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=0.0002, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for i, imgs_hr in enumerate(dataloader):
# 构造对抗标签
valid = torch.ones(imgs_hr.shape[0], 1).requires_grad_.(False)
fake = torch.zeros(imgs_hr.shape[0], 1).requires_grad_.(False)
# 从噪声中采样生成图像
z = torch.randn(imgs_hr.shape[0], latent_dim)
gen_hr = generator(z)
# 训练判别器
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# 计算判别器的损失
real_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(imgs_hr), valid)
fake_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_hr.detach()), fake) # 此处不计算生成器的梯度
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
# 更新判别器参数
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
# 训练生成器
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
g_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_hr), valid)
g_loss += loss_content
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
SRGAN的完整pytorch实现可参考PyTorch-GAN。
3. 实验分析
作者进行了主观打分实验,选择$26$人对不同模型的图像质量进行打分($1$至$5$分),并用得分均值作为平均意见得分(mean opinion score, MOS):

作者比较了不同模型上$4X$超分辨率得到的客观和主观评价指标:



